The Granger (1969) approach to the question of whether 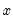 causes
causes 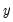 is to see how much of the current
is to see how much of the current 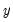 can be explained by past values of
can be explained by past values of 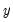 and then to see whether adding lagged values of
and then to see whether adding lagged values of 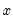 can improve the explanation.
can improve the explanation. 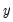 is said to be Granger-caused by
is said to be Granger-caused by 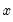 if
if 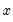 helps in the prediction of
helps in the prediction of 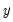 , or equivalently if the coefficients on the lagged
, or equivalently if the coefficients on the lagged 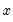 ’s are statistically significant. Note that two-way causation is frequently the case;
’s are statistically significant. Note that two-way causation is frequently the case; 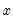 Granger causes
Granger causes 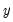 and
and 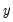 Granger causes
Granger causes 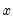 .
.
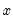 causes
causes 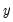 is to see how much of the current
is to see how much of the current 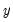 can be explained by past values of
can be explained by past values of 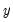 and then to see whether adding lagged values of
and then to see whether adding lagged values of 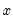 can improve the explanation.
can improve the explanation. 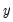 is said to be Granger-caused by
is said to be Granger-caused by 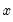 if
if 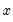 helps in the prediction of
helps in the prediction of 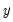 , or equivalently if the coefficients on the lagged
, or equivalently if the coefficients on the lagged 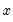 ’s are statistically significant. Note that two-way causation is frequently the case;
’s are statistically significant. Note that two-way causation is frequently the case; 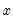 Granger causes
Granger causes 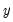 and
and 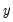 Granger causes
Granger causes 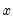 .
. 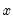 Granger causes
Granger causes 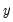 ” does not imply that
” does not imply that 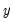 is the effect or the result of
is the effect or the result of 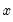 . Granger causality measures precedence and information content but does not by itself indicate causality in the more common use of the term.
. Granger causality measures precedence and information content but does not by itself indicate causality in the more common use of the term. 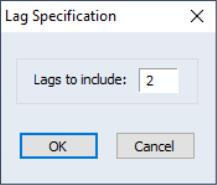
 , that corresponds to reasonable beliefs about the longest time over which one of the variables could help predict the other.
, that corresponds to reasonable beliefs about the longest time over which one of the variables could help predict the other.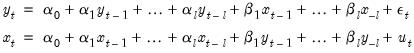
 series in the group. The reported
series in the group. The reported 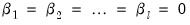
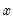 does
does 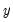 in the first regression and that
in the first regression and that 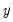 does
does 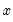 in the second regression.
in the second regression. 