Value-Based Text and Fill Coloring
EViews allows text and fill of individual cells in series and group spreadsheets, and in geomaps. You may specify fixed colors or use the EViews color-mapping engine to assign colors on the basis of values from a series in the workfile. Value-based color-mapping allows users to quickly scan and identify particular observations such as outliers or negative values, or show possible numerical trends.
• For series and group spreadsheets, you may now set the text and/or fill color of each cell You have the option to use a fixed color or to choose colors on the basis of values of a series.
• For geomaps, you may set the fill color of each shape to a fixed color or you may use the colormap to choose colors on the basis of values of a series.
What is a Colormap
A colormap is a set of rules that translate numeric values into colors. The rules are specified in the form threshold values or ranges with descriptions of colors associated with the resulting regions.
EViews offers both predefined colormaps for common settings, as well as the ability to design complex custom colormaps with rules.
You may for example, apply the colormap along with its defaults to a spreadsheet and all negative values will be displayed as red and positive values will be displayed as black. A more complex example would color a series based on values of a different series, with three distinct ranges and gradation between the specified colors.
Defining a Colormap
You will define colormaps when setting the text or fill color for series or group spreadsheets or the fill color for geomaps.
For series spreadsheets, select the or . For group spreadsheets, press the right mouse button while in the spreadsheet view and select either or . For geomaps you will click on , then select the tab.
Once a selection has been made you will be prompted with a dialog similar to:
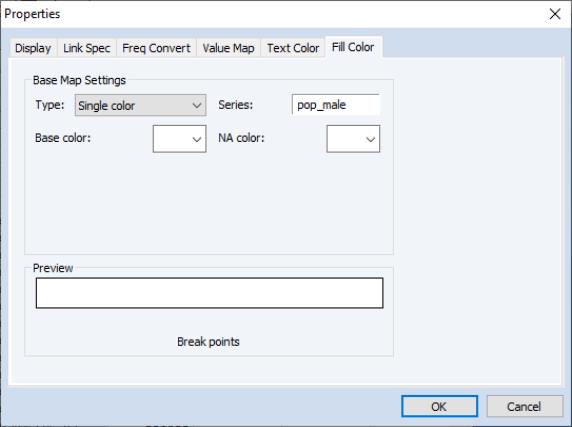
The first dropdown selects which colormap is to be used. EViews offers four pre-defined colormaps (, , and ) and a custom map setting:
• The color colormap will set all NA values to one color and all non-NA values to a base color.
• The colormap places a threshold at zero and will set negative values to a one color, positive values to a another color, and NA values to a third color.
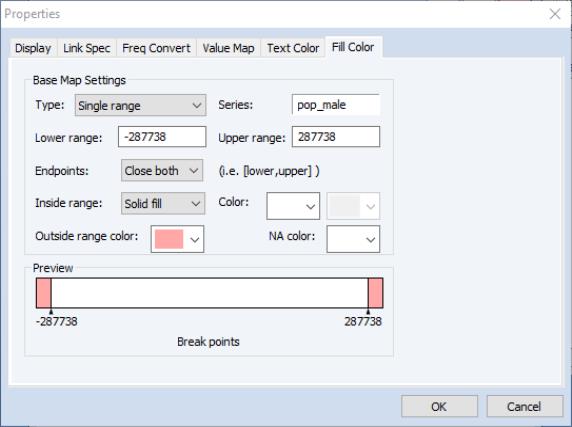
• The map will set values between a specified numerical range to a color, all values outside of the range to a second color, and NA values to a third color.
• The map allows users to identify the high, low, and median observations.
• The last map type is . Custom maps allow for multiple thresholds and multiple ranges. It also provides the ability to blend colors from one threshold to the next or to blend colors between ranges.
Depending on the colormap type that is selected, different options will be made available in the box.
Regardless of the type and settings, a preview of the color map will appear at the bottom of the window. The preview window will show a visual summary of the current color settings. For example, for a colormap where the POP_MALE series values will be used to determine the color, we have:
Here, values of POP_MALE that are greater than -287738 and less than 287738 will be red and all other colors (including NA) will be black. If desired, you can change the range and the applicable colors by modifying the appropriate control.
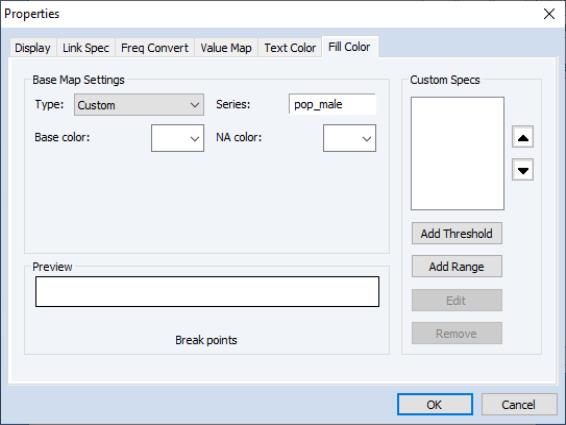
Defining a Custom Colormap
If the pre-defined maps are not adequate for your needs, you may select in the dropdown menu. Custom colormaps allow you to build complex color settings by specifying one or more threshold or range specifications. Custom colormaps also allow you to blend colors between regions.
When a custom colormap type is first chosen, three basic options are available.
• the name of the series or expression whose values will be used to determine the color
• base color used for all elements that are not defined
• the color to be used for NAs
On the right of the dialog is the box and buttons for adding a threshold rule () or a range ().
Note when adding new specification (thresholds and ranges), their effects are additive, meaning the order at which they are listed/used will change behavior. If for example, you were to add two range specs with overlapping values, portions of the first range may be masked by the second.
You may use the up and down arrows to right of the box to change the order of the specs.
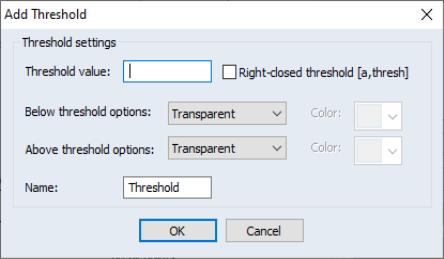
Adding a Custom Threshold
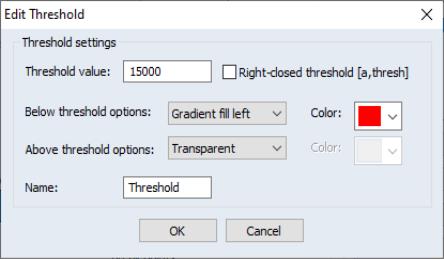
A threshold specification is single user defined value in a custom map whereby you can set the color above and below that value. To add a threshold specification, simply press the button. You will then be prompted for the new threshold configuration settings:
• The edit field contains the value.
• The and drop down controls the application of color.
You may determine whether the colors remain unchanged () and if not, if the colors should be solid () or if they should blend to the previous color. For the below threshold, the gradient will blend the selected color to the existing color from the threshold value to the left (), while the above threshold will blend from the threshold value to the right ().
To the right of these settings are the color selection controls where you may specify the below and above threshold colors.
• The checkbox indicates whether the exact threshold value should use the below or above threshold color settings. By default, the threshold value uses the “above” settings.
• The threshold specification provides a name which may aid in identifying this setting in the colormap dialog.
Here, we have set a threshold at 15,000 the values equal to and below 15,000 should be red but blend to the previous threshold or range. The threshold settings specify that all values above 15,000 use whatever colors are already specified in the map:
Adding a Range Specification
A range specification is defined by two user-defined values which create three regions: a within range, an above range, and a below range.
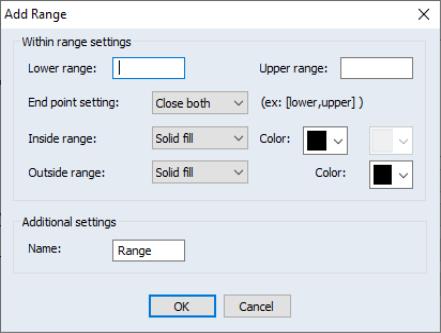
To add a new range, simply click the button. You will be prompted to specify range configuration settings:
• The and edit fields define the range limits.
• The and drop down controls the application of color.
You may determine whether the colors remain unchanged () and if not, if the colors should be solid () or if they should be a gradient ().
To the right of these settings are the color selection controls where you may specify the below and above threshold colors.
If you choose a gradient for the inside range, you will be prompted for both the bottom and top color of the range.
• The drop-down menu indicates whether the left and right ends of the range are included in the range or are outside of the range.
• The threshold specification provides a name which may aid in identifying this setting in the colormap dialog.
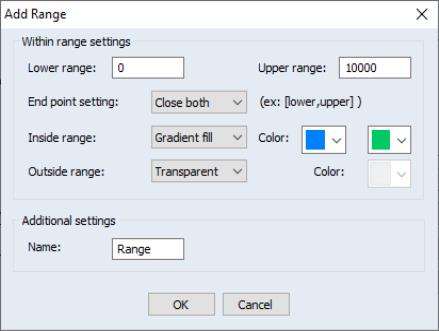
Finally, press to save the range specification. For our example, we will set the lower range to be 0, the upper range to 10,000 with blue and green respectively. The outside of the range is set to be transparent.
Multiple Specifications
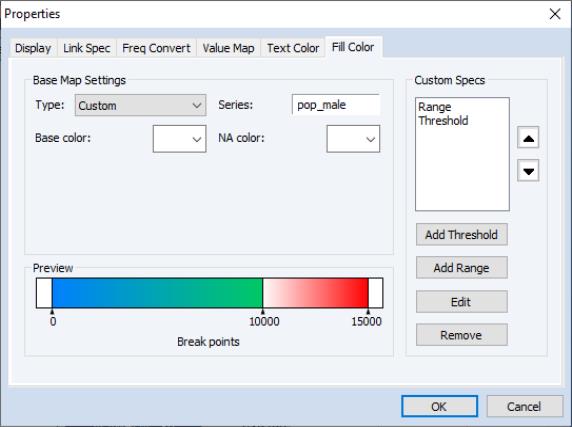
After applying both the and examples, the resultant map will be:
Values below 0 will be white. From 0 to 10,000 will blend from red to green and from 10,000 to 15,000 will blend from white to red. Lastly, values greater than 15,000 will be white.
We remind you the effects of custom specifications is additive, meaning the order at which they are listed/used will change behavior. If for example, you were to add two range specs with overlapping values, portions of the first range may be masked by the second.
You may use the up and down arrows to right of the box to change the order of the specs.