Cholesky factor of matrix.
Syntax: @cholesky(s)
s: sym
Return: matrix
Returns a matrix containing the Cholesky factorization of
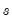
.
The Cholesky factorization finds the lower triangular matrix
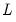
such that
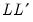
is equal to the symmetric source matrix
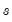
.
Examples
sym s = @inner(@mrnd(10, 10))
matrix chol = @cholesky(s)
matrix orig1 = chol * chol.@t
sym orig2 = @inner(chol.@t)
computes the Cholesky, and uses it to recreate the original matrix. Note that ORIG1 is a matrix object whereas ORIG2 is a sym object.
Inverting the Cholesky may be used to obtain the matrix inverse.
sym sinv1 = @inverse(s)
matrix invchol = @inverse(chol)
matrix sinv2 = invchol.@t * invchol
sym sinv3 = @inner(invchol)
matrix id1 = sinv1 * s
matrix id2 = sinv2 * s
matrix id3 = sinv3 * s
uses properties of the inverse of the Cholesky to recreate the matrix inverse so that ID1, ID2, and ID3 are all different computations yielding the identity matrix.
Cross-references
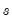 .
.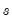 .
.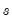 .
.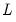 such that
such that 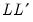 is equal to the symmetric source matrix
is equal to the symmetric source matrix 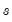 .
.