Cumulative variances (population – non-d.f. adjusted) of a series.
Equivalent to @cumvarp.
Increasing samples calculation of the population (non-d.f. adjusted) Pearson product moment variance.
Syntax: @cumvar(x, [s])
x: series
s: (optional) sample string or object
Return: series
The population variance for each observation
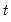
is calculated as
where
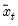
is the mean of
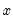
over the first
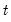
observations.
This function is panel aware.
Examples
series x = @nrnd
group g @cumvar(x) @cumvars(x) @cumvarp(x)
g.line
plots @cumvar(x), @cumvars(x), and @cumvarp(x) together. Note that @cumvar(x) and @cumvarp(x) are equivalent. All three series converge in probability to 1.
Cross-references
For the backward variant of this function, see
@cumbvar.
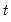 is calculated as
is calculated as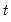 is calculated as
is calculated as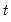 is calculated as
is calculated as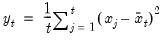
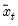 is the mean of
is the mean of 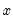 over the first
over the first 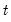 observations.
observations.