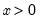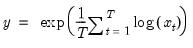Function Reference: G
@gamma (Complete) gamma function.
@gammader First derivative of the gamma function.
@gammalog Natural logarithm of the gamma function.
@getnextname String containing next available name in the workfile.
@grid Vector containing equally spaced grid of values.
(Complete) gamma function.
Syntax: @gamma(x)
x: number
Return: number
for
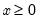
.
Related, stable calculations for the logarithm of @gamma may be obtained using
@gammalog.
Examples
= @gamma(5)
returns 24 (equivalent to
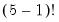
).
= @gamma(0.5)
returns 1.77245... (equivalent to
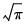
).
Cross-references
Derivative (first) of the gamma function.
Syntax: @gammader(x)
x: number
Return: number
for
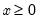
.
Note: Euler’s constant, 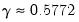 , may be evaluated as
, may be evaluated as 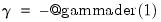 .
. Examples
= @gammader(1)
returns -0.57721....
Cross-references
See also
@gamma and
@digamma.
Incomplete gamma function.
Syntax: @gammainc(x, a[, u])
x: number
a: number
u: (optional) number
Return: number
for 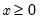 and
and 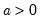 .
. If the optional argument u is non-zero, return the upper-tail value:
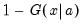 | (18.7) |
Examples
= @gammainc(1,1)
returns 0.63212... (equivalent to
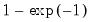
).
Cross-references
Derivative of the incomplete gamma integral.
Syntax: @gammaincder(x, a, c)
x: number
a: number
c integer
Return: number
Given the incomplete gamma integral for elements of x and a:
for
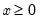
and
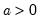
, compute the derivative given by
c where
c is an integer from 1 to 5 indicating the desired derivative,
If
c is not an integer, the integer floor
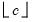
will be used.
Examples
= @gammaincder(1,3,1)
returns 0.18393....
Cross-references
Inverse of the incomplete gamma function.
Syntax: @gammainciv(p, a)
x: number
p: number
a: number
Return: number
Find the value of
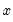
satisfying:
for 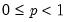 and
and 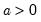 .
. Examples
= @gammaincinv(0,2)
returns 0.
Cross-references
Natural logarithm of the gamma function.
Syntax: @gammalog(x)
x: number
Return: number
for
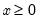
.
Examples
= @gammalog(3)
returns 0.69314....
Cross-references
Extract main diagonal from matrix.
Syntax: @getmaindiagonal(m)
m: matrix, vector, sym
Return: vector
Returns a vector created from the main diagonal of the matrix or sym object. The main diagonal is defined as the elements {(1, 1), (2, 2), ..., (k, k)} of the matrix, where k is the smaller of the number of rows and columns.
Examples
If M1 is an
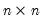
identity matrix, then
= @getmaindiagonal(m1)
returns an n-vector of ones.
Cross-references
Syntax: @getnextname(str)
str: string,
Return: string
Returns a string containing the next available variable name in the workfile, starting with str (i.e. entering “result” will return “RESULT01” unless there is already a RESULT01, in which case it will return “RESULT02”).
Examples
%objname = @getnextname("eqtest")
equation {%objname}.ls y c x1 x2 x3
assigns the next available name to the string variable %OBJNAME, and then uses the name to estimate an equation in the workfile.
Cross-references
Object type of active object (_this)
Syntax: @getthistype
Return: string
If no workfile is open, or if no object has yet been opened in a workfile, the function will return the string "NONE".
This latter behavior is in contrast to using the data member syntax “_this.@type”, which will generate an error in cases like this where the active object is undefined.
Cross-references
See also the
@type data member of each object in
“Object View and Procedure Reference”.
See
“The Active Object Keyword” for a discussion of the _THIS active object.
Geometric mean.
Computes the geometric mean of the elements of
x for
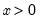
Syntax: @gmean(x[, s])
x: series, vector, matrix
s: (optional) sample string or object when x is a series and assigning to a series
Return: number
The geometric mean is calculated as
For series calculations, EViews will use the current or specified workfile sample.
Examples
If x is a series of length 3 with elements 1, 2, and 4, then
= @gmean(x)
returns 2 (= the cube root of 8).
Cross-references
See also
@mean,
@hmean, and
@trmean.
Vector containing equally spaced grid of values.
Syntax: @grid(d1, d2, n)
d1: number
d2: number
n: integer
Return: vector
Returns a vector holding an arithmetic sequence of n elements. The initial element has value d1, the last element is d2, and there are equal increments between rows of the vector.
Examples
vector v1 = @grid(0, 3, 10)
creates V1, a 10-element vector with first element 0, last element 3, and equal increments between successive rows of the vector.
vector cdf1 = @cnorm(@grid(-2.0, 2.0, 401))
creates a 401-element vector of normal CDF ordinates evaluated at points from -2.0 to 2.0.
Cross-references
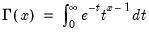
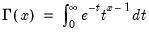
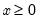 .
.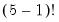 ).
).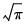 ).
).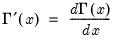
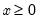 .
.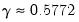 , may be evaluated as
, may be evaluated as 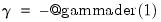 .
.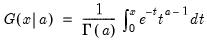
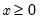 and
and 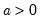 .
.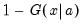
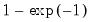 ).
).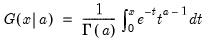
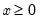 and
and 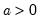 , compute the derivative given by c where c is an integer from 1 to 5 indicating the desired derivative,
, compute the derivative given by c where c is an integer from 1 to 5 indicating the desired derivative,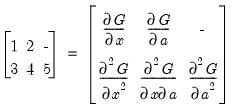
 will be used.
will be used.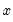 satisfying:
satisfying: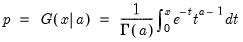
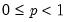 and
and 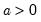 .
.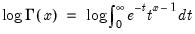
 .
.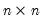 identity matrix, then
identity matrix, then