Function Reference: Q
@qbeta Beta distribution quantile.
@qbinom Binomial distribution quantile.
@qchisq Chi-square distribution quantile.
@qexp Exponential distribution quantile.
@qextreme Extreme value (Type I-minimum) distribution quantile.
@qgamma Gamma distribution quantile.
@qged Generalized error distribution quantile.
@qnegbin Negative binomial distribution quantile.
@qnorm Standard normal distribution quantile.
@qtdist Student’s
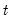
distribution quantile.
@quantilesby Empirical quantiles of a series for each specified group.
@quarter Quarter of the year of the observation.
@qunif Uniform distribution quantile.
@qweib Weibull distribution quantile.
Beta distribution quantile.
Syntax: @qbeta(p, a, b)
p: number,
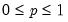
a: number,
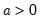
b: number,
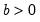
Return: number
Find the x satisfying
where
and 0 elsewhere, and
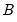
is the beta function
Examples
= @qbeta(0.75, 1, 2)
returns 0.5.
Cross-references
See also
@cbeta,
@dbeta, and
@rbeta.
Binomial distribution quantile.
Syntax: @qbinom(v, n, p)
v: number,
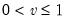
n: integer,
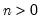
p: number,
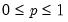
Return: integer
Find value with cumulative probability exceeding
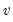
.
Returns smallest integer
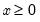
satisfying
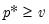 where
whereis the cumulative probability function evaluated at
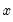 ,
, Examples
= @qbinom(0.5, 5, 0.5)
returns 2.
Cross-references
Chi-square distribution quantile.
Syntax: @qchisq(p, v)
p: number,
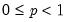
v: number,
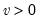
Return: number
Find the x satisfying
where
Examples
= @qchisq(0.5, 100)
returns 99.33412....
Cross-references
Exponential distribution quantile.
Syntax: @qexp(p, m)
p: number,
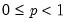
m: number,
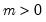
Return: number
Return the
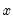
satisfying
so that
Examples
= @qexp(0.5, 1)
returns 0.69314... (equal to log(2)).
Cross-references
See also
@cexp,
@dexp, and
@rexp.
Extreme value (Type I-minimum) distribution quantile.
Syntax: @qextreme(p)
p: number,
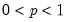
Return: number
Return the
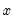
satisfying
so that
Examples
= @qextreme(0.5)
returns -0.36651....
Cross-references
F-distribution quantile.
Syntax:
@qfdist(
p, 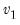 ,
, 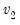 )
) p: number
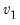
: number,
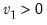
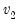
: number,
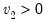
Return: number
For
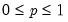
, find the
x satisfying
where,
for
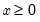
and 0 otherwise, and
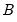
is the beta function
Examples
= @qfdist(0.5, 2, 2)
returns 1.
Cross-references
Quadratic form.
Syntax: @qform(s, o)
s: sym
o: vector, matrix, sym
Return: number, sym
Returns the quadratic form of a symmetric matrix s, with a vector or matrix object o.
• if o is a vector, the function returns a scalar
• If o is a matrix, the function returns a sym
Examples
sym s1 = @inner(@mnrnd(20, 4))
vector v1 = @mrnd(4)
scalar q1 = @qform(@inverse(s1), v1)
generates a symmetric matrix S1, then computes the quadratic form using the inverse of S1, and the randomly generated vector V1.
matrix m1 = @mrnd(4, 5)
sym q2 = @qform(@inverse(s1), m1)
computes the matrix form of the quadratic form, returning a sym.
Cross-references
See also
@inner and
@outer.
Gamma distribution quantile.
Syntax: @qgamma(p, b, r)
p: number,
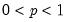
b: number,
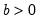
r: number,
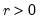
Return: number
Return the
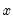
satisfying
where
for
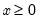
and 0 elsewhere.
Examples
= @qgamma(0.5, 4, 1)
returns 2.77258....
Cross-references
Generalized error distribution quantile.
Syntax: @qchisq(p, r)
p: number,
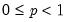
r: number,
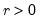
Return: number
Find the x satisfying
where
Examples
= @qged(0.75, 2)
returns 0.67448....
Cross-references
See also
@cged,
@dged, and
@rged.
Laplace distribution quantile.
Syntax: @qlaplace(p)
p: number
Return: number
Return the
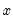
satisfying
where
Examples
= @qlaplace(0.25)
returns -0.69314....
Cross-references
Logistic distribution quantile.
Syntax: @qlogistic(p)
p: number,
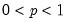
Return: number
Return the
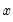
satisfying
so that
Examples
= @qlogistic(0.5)
returns 0.
Cross-references
Log normal distribution quantile.
Syntax: @qchisq(p, m, s)
p: number,
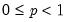
m: number,
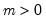
s: number,
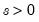
Return: number
Find the x satisfying
where
Examples
= @qlognorm(0.5, 0, 2)
returns 1.
Cross-references
Negative binomial distribution quantile.
Syntax: @qnegbin(v, n, p)
v: number,
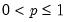
n: number,
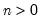
p: number,
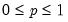
Return: integer
Find value with cumulative probability exceeding
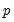
.
Returns smallest integer
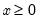
satisfying
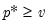 where
whereis the cumulative probability function evaluated at
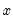 ,
, Examples
= @qnegbin(0.5, 10, 0.5)
returns 9.
Cross-references
Standard normal distribution quantile.
Syntax: @qnorm(p)
p: number
Return: number
Return the
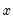
satisfying
where
Examples
= @qnorm(0.95)
returns 1.64485....
Cross-references
Pareto distribution quantile.
Syntax: @qpareto(p, m, a)
p: number,
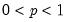
m: number,
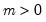
a: number,
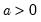
Return: number
Return the
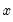
satisfying
Examples
= @qpareto(0.75, 1, 2)
returns 2.
Cross-references
Poisson distribution quantiles.
Syntax: @qpoisson(p, m)
p: number,
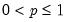
m: number,
Return: integer
Find value with cumulative probability exceeding
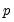
.
Returns smallest integer
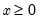
satisfying
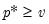 where
whereis the cumulative probability function evaluated at
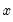 ,
, Examples
= @qpoisson(0.5, 10)
returns 10.
Cross-references
QR decomposition.
Syntax: @qr(M, R[, P])
M: matrix
R: matrix
P: (optional) matrix
Return: matrix
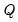
Decomposes an
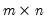
matrix
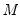
into an
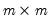
orthogonal matrix
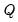
and an
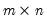
upper triangular matrix
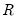
such that
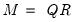
, where
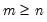
.
If permutation matrix
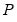
is provided, the decomposition produces
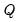
and
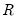
such that
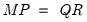
.
Examples
matrix m1 = @mnrnd(7, 5)
matrix r
matrix q = @qr(m1, r)
generates a random matrix M1, then decomposes it into the orthogonal matrix Q, and the upper triangular matrix R.
The following illustrate the properties of the decomposition:
sym i1 = @inner(q)
matrix m2 = q * r
where I1 is the identity matrix, and M2 is equal to M1.
Cross-references
Student’s
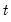
distribution quantile.
Syntax: @qtdist(p, v)
p: number,
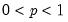
v: number,
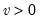
Return: number
Return the
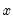
satisfying
where
Examples
= @qtdist(0.025, 1)
returns -12.70620....
Cross-references
Empirical quantile.
Compute the quantile value where approximately 100*q percent of the data is less than or equal to the value,
Syntax: @quantile(x, q[, m, s])
x: series, vector, matrix
q: number, series, vector, matrix
m: (optional) string
s: (optional) sample string or object when x is a series and assigning to a series
Return: number
• The quantile value
q must satisfy
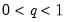
.
• m is an optional string controlling the method of calculating the empirical distribution function: “b” (Blom), “r” (Rankit-Cleveland), “o” (Ordinary), “t” (Tukey), “v” (van der Waerden), “g” (Gumbel). The default value is “r”.
Rankit-Cleveland (default) | |
Ordinary | |
Van der Waerden | |
Blom | |
Tukey | |
Gumbel | |
To compute the
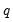
-quantile, first find
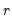
, the smallest rank such that,
where the order statistics
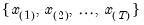
represent data for the
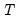
observations ordered from low to high, and
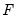
is the assumed empirical distribution function. For purposes of computing
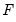
, tied ranks are assumed to take the last tied value.
Then the quantile is computed as
where the interpolating constant is
for
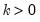
the smallest integer where
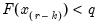
. In the leading case where there are no tied
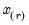
values,
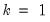
.
For series calculations, EViews will use the current or specified workfile sample.
Examples
= @quantile(x, 0.5)
returns the median of the series x.
= @quantile(x, 0.1)
returns the first decile (10th percentile) of the series x.
Cross-references
Empirical quantiles of a series for each specified group.
Syntax: @quantilesby(x, y[y1, y2, ... yn], q, [s])
x: series
y: series, alpha
q number
s: (optional) sample string or object
Return: series
Returns the
q-th quantile of
x for each group defined by distinct values of y. The quantiles will be computed using the Rankit-Cleveland definition (see
@quantile)
. EViews will use the current or specified workfile sample.
Examples
show @quantilesby(x, g1, g2, 0.25)
produces a linked series of the by-group 25th percentiles of the series x, where members of the same group have identical values for both g1 and g2.
Cross-references
Quarter of the year of the observation.
Syntax: @quarter
Return: series
Returns the quarter of the year (1–4) associated with each observation in the workfile.
• If the workfile is of lower than quarterly frequency, all observations will be set to 1.
• If the workfile is undated, observations will be set to -1.
Examples
series dt = @quarter
saves the quarter into the series DT.
The command
smpl if @quarter = 4
sets the sample to only include fourth quarter observations.
Cross-references
Uniform distribution quantile.
Syntax: @qunif(p, a, b)
p: number,
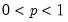
a: number
b: number,
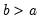
Return: number
Return the
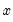
satisfying
so that
Examples
= @qunif(0.4, 1, 6)
returns 3.
Cross-references
See also
@cunif,
@dunif, and
@runif.
Weibull distribution quantile.
Syntax: @qweib(p, m, a)
p: number,
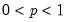
m: number,
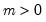
a: number,
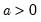
Return: number
Return the
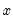
satisfying
Examples
= @qweib(0.5, 1, 1)
returns 0.69314... (the natural log of 2).
Cross-references
See also
@cweib,
@dweib, and
@rweib.
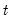 distribution quantile.
distribution quantile.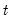 distribution quantile.
distribution quantile.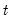 distribution quantile.
distribution quantile.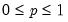
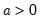
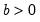
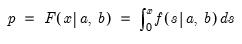
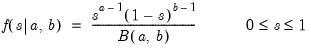
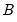 is the beta function
is the beta function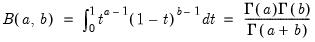
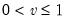
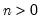
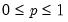
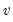 .
.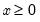 satisfying
satisfying 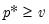 where
where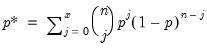
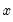 ,
, 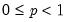
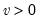
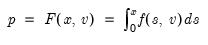
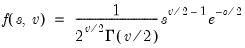
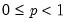
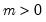
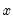 satisfying
satisfying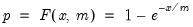
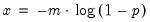
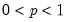
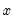 satisfying
satisfying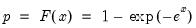
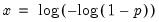
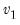 ,
, 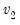 )
)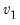 : number,
: number, 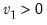
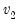 : number,
: number, 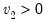
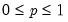 , find the x satisfying
, find the x satisfying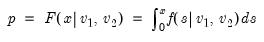
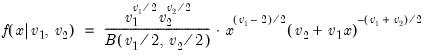
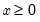 and 0 otherwise, and
and 0 otherwise, and 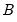 is the beta function
is the beta function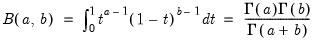
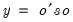
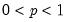
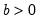
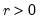
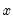 satisfying
satisfying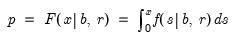
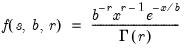
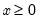 and 0 elsewhere.
and 0 elsewhere.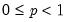
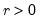
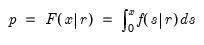
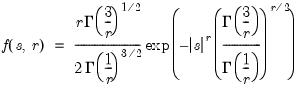
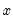 satisfying
satisfying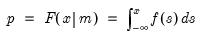
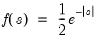
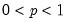
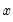 satisfying
satisfying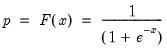
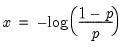
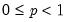
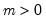
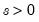
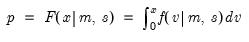
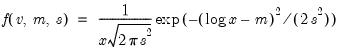
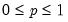
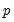 .
.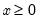 satisfying
satisfying 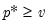 where
where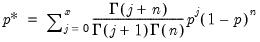
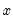 ,
, 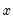 satisfying
satisfying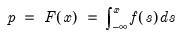
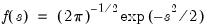
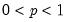
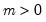
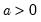
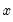 satisfying
satisfying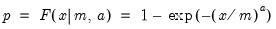
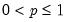
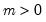
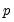 .
.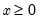 satisfying
satisfying 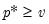 where
where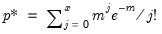
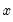 ,
, 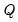
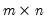 matrix
matrix 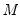 into an
into an 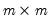 orthogonal matrix
orthogonal matrix 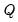 and an
and an 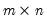 upper triangular matrix
upper triangular matrix 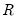 such that
such that 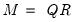 , where
, where 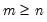 .
. 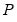 is provided, the decomposition produces
is provided, the decomposition produces 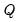 and
and 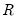 such that
such that 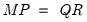 .
. distribution quantile.
distribution quantile.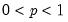
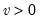
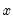 satisfying
satisfying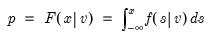
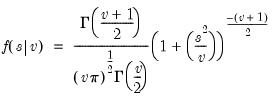
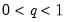 .
.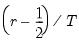
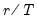
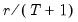
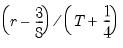
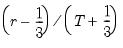
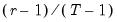
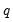 -quantile, first find
-quantile, first find 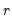 , the smallest rank such that,
, the smallest rank such that,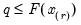
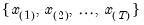 represent data for the
represent data for the 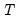 observations ordered from low to high, and
observations ordered from low to high, and 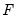 is the assumed empirical distribution function. For purposes of computing
is the assumed empirical distribution function. For purposes of computing 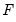 , tied ranks are assumed to take the last tied value.
, tied ranks are assumed to take the last tied value.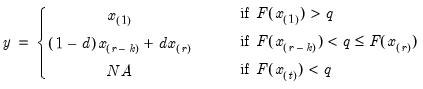
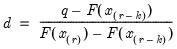
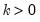 the smallest integer where
the smallest integer where 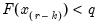 . In the leading case where there are no tied
. In the leading case where there are no tied 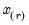 values,
values, 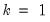 .
.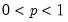
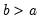
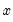 satisfying
satisfying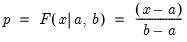
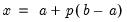
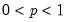
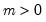
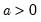
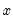 satisfying
satisfying